PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
PRODUCT CENTER
产品中心
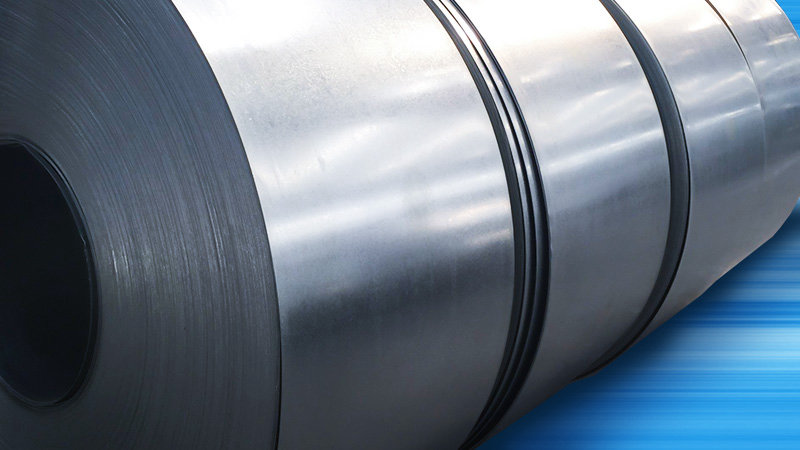
产品简介


PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY
生产工艺
The typical production process of cold-rolled steel strip hot-dip galvanizing is:
Loading → uncoiling → pinch, straightening → welding → surface pre-cleaning → inlet looper → annealing → hot-dip galvanizing → alloying → cooling → middle looper → smoothing → stretching and bending straightening → post-processing → inspection Take-up.
Continuous annealing furnace shell:
Generally, ceramic fiber outsourcing stainless steel plates are used, refractory bricks and heat-insulating bricks are used for the furnace bottom, and the furnace rolls are driven separately and frequency-converted. Generally, the annealing furnace is composed of a preheating section, a heating section, a cooling section, and a zinc pot inlet section. In the first three sections, a mixed gas of hydrogen and nitrogen is introduced to heat the strip steel to above the recrystallization temperature in this reducing atmosphere, and Heat preservation, soaking, and cooling make the strip steel sealed into the zinc pot for hot-dip galvanizing.
There are two main purposes: one is to achieve recrystallization annealing of the strip to eliminate rolling stress, restore the grain structure, and improve the plasticity of the strip; the second is to make the steel have a clean and oxide-free active surface, so that it has a very High plating adhesion.
Huajing Galvanized Line
Production process of continuous hot-dip galvanizing unit

| S/N | Content | S/N | Content |
01 | Unbook | 08 | Zinc pot |
| 02 | Straighten | 09 | Zinc layer annealing furnace |
| 03 | Cut | 10 | Air knife |
| 04 | Welding | 11 | Smooth |
| 05 | Preheating section | 12 | Stretch straightening |
| 06 | Heating section | 13 | Chemical treatment |
| 07 | Cooling section | 14 | Take-up |
POST PROCESSING
后期处理
The post-treatment of galvanized steel strip includes three aspects: passivation, pre-phosphating and oiling. First of all, passivation treatment of the galvanized steel strip can improve the surface structure and gloss of the galvanized layer, increase the corrosion resistance and service life of the galvanized layer, and improve the bonding force between the coating and the base metal. The passivation treatment mainly uses chromate passivation. Add some activators, such as fluoride, phosphoric acid or sulfuric acid to the passivation solution, so that a thick chromate film can be obtained after passivation. When there is fluoride in the passivation solution, it can reduce the surface tension of the steel strip, accelerate the film-forming reaction, and increase the chemical polishing effect, making the passivation film fine and bright.
The application effect of galvanized steel strip meets modern needs and is now widely used as a building material. Galvanized steel strip has the characteristics of being rust-free and corrosion-resistant for many years. It can be protected from the external adverse environment and always maintain its own performance and appearance. In the process of using galvanized steel strip, in order to improve its operating efficiency and its own characteristics, the finished product of galvanized steel strip can be post-treated to make its performance better.

PRODUCT USE
产品用途
Galvanized steel strip is generally used to make steel pipes, such as greenhouse pipes, drinking water pipes, heating pipes, gas delivery pipes; it can also be used in construction, light industry, automobiles, agriculture, animal husbandry, fishery, and commerce.
Among them, the construction industry is mainly used to manufacture anti-corrosion industrial and civil building roof panels, roof grills, etc.; the light industry uses it to manufacture household appliance shells, civil chimneys, kitchen appliances, etc., and the automobile industry is mainly used to manufacture corrosion-resistant parts for cars. ;Agriculture, animal husbandry and fishery are mainly used as food storage and transportation, meat and aquatic products frozen processing tools, etc.; commercial mainly used as material storage and transportation, packaging tools; steel structure sandalwood (C, Z steel); light steel keel, suspended ceiling Keel and so on.

